Classification of bones, types of bones
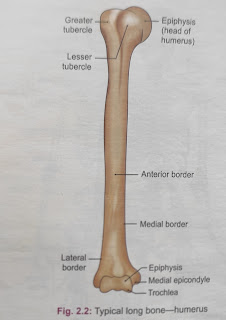
Types of Bones Long bones:- These serve as levers for the muscle action. E.g. Femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, ulna etc. Short bones:- their shape is usually cuboid, (like a cube) or scaphoid (boat shaped). E.g. Tarsal and carpal bones Flat bones: -These consists of parallel layer of compact bone separated by a thin layer of cancellous bone tissue E.g. scapula, skull, pelvic bone etc. Irregular bones:- These have a peculiar and irregular shape and are unique in their appearance and function. E. g Hip bone, bones in base of skull, e. g. Sphenoid & 1st &2nd cervical vertebrae Pneumatic bones: - Certain irregular bones contain large air spaces lined by epithelium E. g. Maxilla, sphenoid, ethmoid, etc., Sesamoid bones:- These are bony nodules found embedded in the tendons or joint capsules. E. g:- Patella in the tendon of quadriceps femoris, pisiform in the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris, flabella in the tendon of lateral head of gastrocnemius,...